Contents
- 1 FFC(Flexible flat cable)
- 2 Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC)
- 3 FFC vs FPC: Application Differences
- 4 FFC vs FPC: Production Difference
- 5 FFC vs FPC: Thickness
- 6 FFC vs FPC: Strict Production Standards
- 7 FFC vs. FPC: Different Types
- 8 FFC vs FPC: Line Layout
- 9 FFC vs FPC: Unique Functionality-Inability to Replace Each Other
- 10 FPC vs FFC: Connectors
- 11 Summary
FFC(Flexible flat cable)
Flexible flat cable, or FFC, is an electric cable that’s both flexible and flat. This cable is
a descendant of ribbon cables but in miniature forms.
Some of the most basic uses of such
types of wires are high-density consumer electronics.
These include cell phones and laptops
and consist of pitch options that range from 0.5mm to 2.54mm.
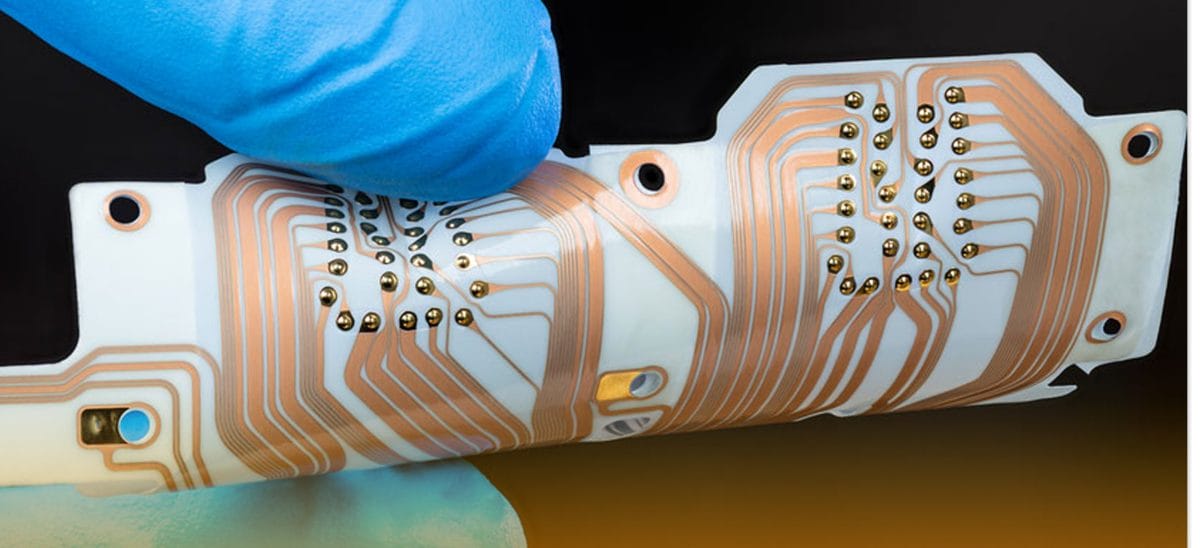
Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC)
A flexible printed circuit or an FPC, in short, is somewhat a bit complex compared to the FFC circuit. These describe those circuits that can effectively incorporate components. Build them on flexible materials.
FPC is typically made of the copper conductor circuit and etching a polyimide material.
While FFCs can function well in harsh conditions, FPCs can easily handle even tougher conditions and are found in 0.3mm versions.
Flexible printed circuits are used in almost all rigid printed circuit boards. Their main aim is to provide excellent flexibility to the board or electronic packages that are tightly assembled.
Several types of FPCs exist, such as double-sided, single-layer, and flex multilayer circuits.
Single-sided flex circuits- consist of only one conductor layer. Double-sided FPCs – are those flexible circuits that come with two layers of conductors.
Flexible circuits have three or more conducting layers. They are also known as multilayer flexible circuit boards.
Mostly, plated through holes interconnect all these layers. Although this is not necessary, openings can be made to access lower parts of the circuit.
FFC vs FPC: Application Differences
FFC vs FPCs differ mainly in their applications.
FPCs are better suited for applications that need minimal space due to their 0.15 mm-0.2 mm thickness range, while FFCs use more space in electrical household consumer goods.
Due to their utility in sensitive applications, FPCs typically employ a stricter quality standard than FFCs. Also, FFCs have more connector options than FPCs. However, you can have FCP- FCP and FCP-FFC connector mating instead of only FFC-FFC.
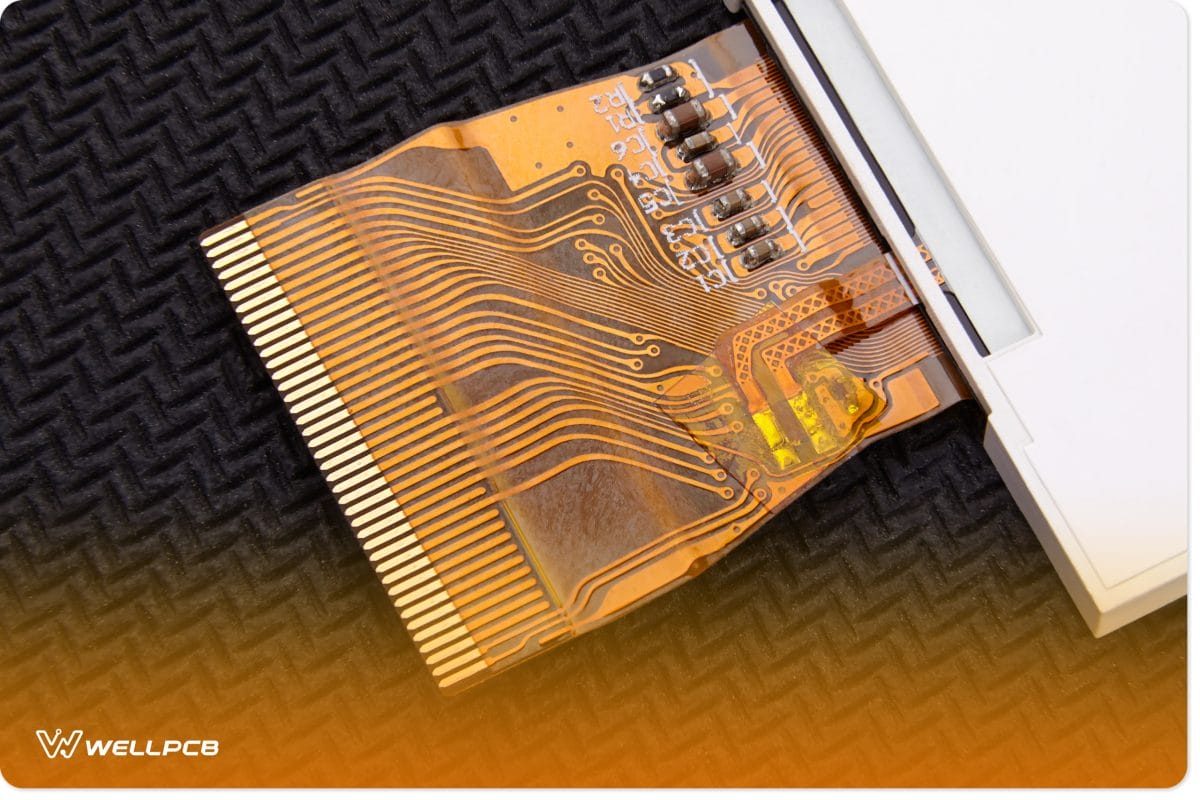

FFC vs FPC: Production Difference
Flexible flat cables also differ from Flexible printed circuits in terms of production methods. FPCs are manufactured by etching on the Flexible Copper Clad Laminate (FCCL) and then laminated into different layers. But FFC entails a simple lamination of flat polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and copper wires.
For this reason, flexible flat cables tend to be a bit thicker and more significant than flexible printed cables. Unlike FPCs, FFCs are made with such wires using two layers that sandwich the insulating foil on the flat copper conductor.
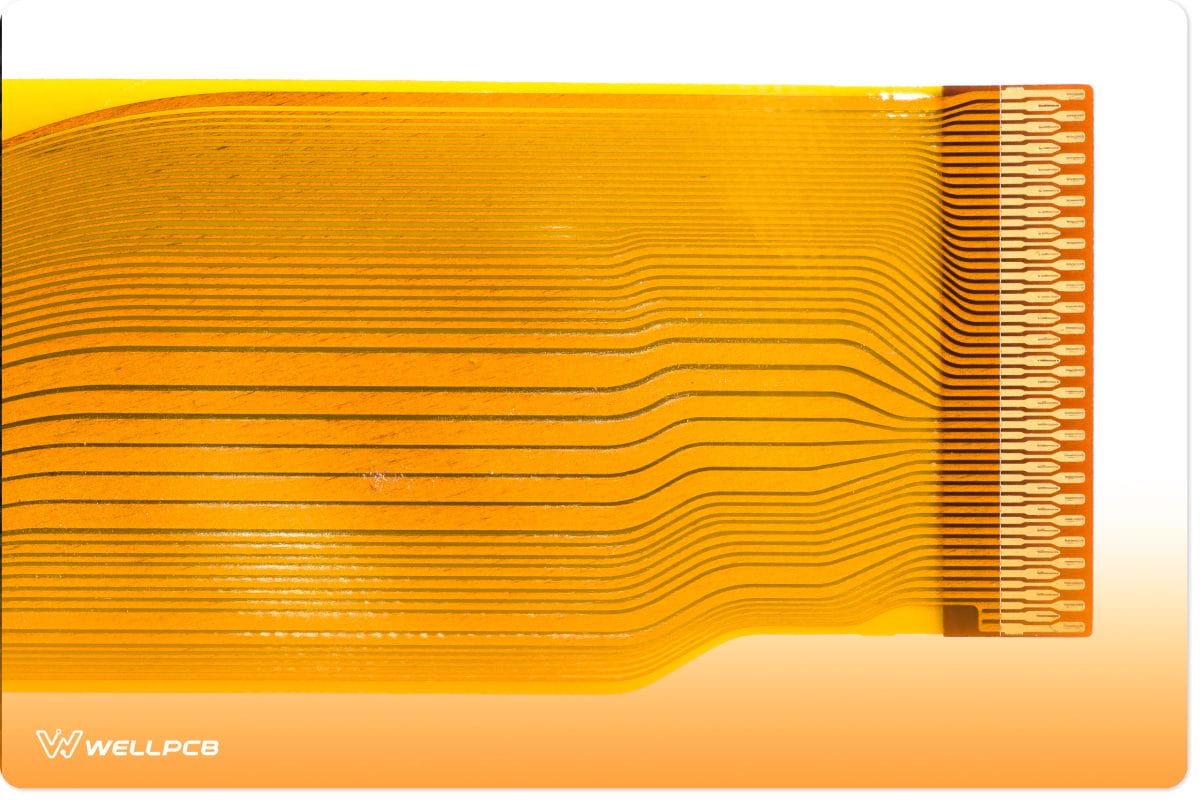

FFC vs FPC: Thickness
As mentioned earlier, there are several application areas where FFCs would work well compared to flexible printed circuits.
For instance, tight fields need cables of a more significant thickness compared to using such cables in applications that are not highly demanding.
FFC cables designed to work in harsh environmental conditions have their ideal thickness space of 0.5mm, 0.8mm,1.0mm,1.25mm,1.27mm,1.5mm,2.0mm, and 2.54mm.
On the other hand, FPC cables take little space, and many of them are between 0.15 mm and 0.2 mm thick.
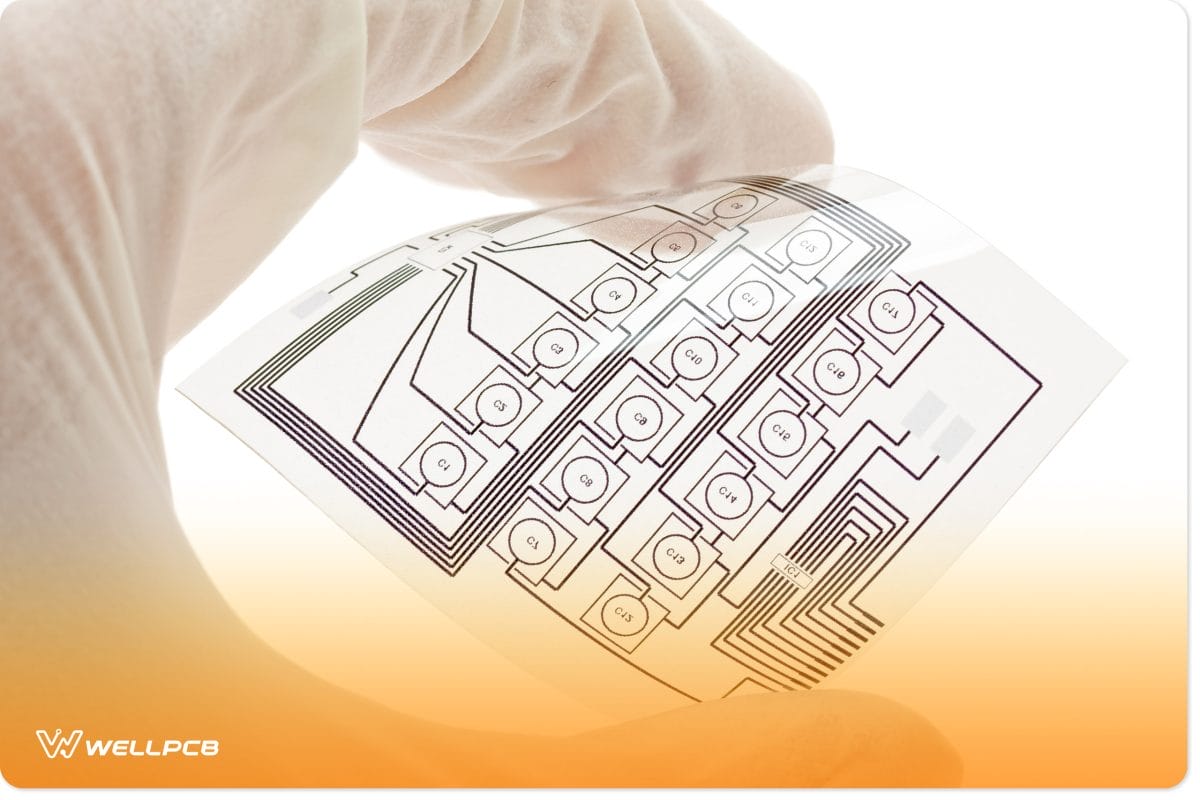

FFC vs FPC: Strict Production Standards
As you can remember, flexible printed circuits are conventional within most people and applications across the.
For this reason, their manufacturing standards are a little bit strict when compared to flexible flat cables.
Most military and medical applications rely heavily on FPCs instead of FFCs.
Manufacturers have to ensure that they employ the required standards when producing FPC.
The idea behind this is a majority of them serve in critical medical, aerospace, or even medical appliances.
Equipment that may end up saving human life. Most FPCs undergo stringent quality tests before their release to the market.
FFCs aren’t subject to strict production and quality measures.

FFC vs. FPC: Different Types
Unlike flexible flat cables, several types of flexible printed circuits are highlighted below.
1. Single-layer circuits – also known as single-sided circuits. These come with only a single conductor layer of metal-filled polymer or metal on a flexible dielectric film. These are cheap to manufacture compared to the rest.
2. Double-sided – as the name suggests, these are flexible circuits. They consist of two layers of conductors.
3. Multilayer flexible circuits have three or more additional layers of conductors. Some have four layers, others up to six layers, and others may have more than ten layers. They are expensive to manufacture compared to single- and double-layer flex circuits. Additionally, multilayer flex circuits can come in various shapes and sizes.
FFC vs FPC: Line Layout
If you are keen enough, you will notice some differences in the line layout between FFCs and FPCs. Line layout is another key difference separating these two circuit types.
Flexible printed circuit boards are for use where there is much bending and twisting. You will notice that the line layout is somewhat horizontal.
However, most flexible flat cables have a vertical line layout. This is because most people are familiar with flexible printed circuit boards, where bending or twisting is uncommon.
Again, differences in line layout between flexible flat cables and flexible printed circuits are another differentiating factor.
FFC vs FPC: Unique Functionality-Inability to Replace Each Other
Lastly, the failure to replace each other or fit where another can work while functioning as desired differentiates flexible printed circuits from flexible flat cables.
For instance, their production systems are different from each other. Also, flexible printed circuits are slightly vulnerable compared to flexible flat cables.
Still, flexible flat cables encompass materials that are good conductors of heat. As such, it’s almost impossible for one to fit into the role of another one.
Thus, the inability to replace each other is another essential factor between FFCs and FPCs.
FPC vs FFC: Connectors
FPC and FFC differ in the types of connectors that enable their function.
Unlike FPCs, FFC connectors only work when you mate them with other FFC connectors.
You can mate FPCs to FFCs and FFC, making them more expensive yet versatile in applications.
Also, you can use FPCs with I/O connectors to form connections to exterior devices.
Various structurally different types of FFC connectors dictate where you can use them.
For example, Type A FFC connectors have a reinforcing plate on the tape.
There are also Type E FFC connectors in which only one side of the reinforcing tape is bonded to the insulating tape, while the other end has direct soldering.
Type G FFC connectors have direct soldering on the two ends.
For FPC connectors, you can differentiate based on insertion force, i.e., the effort you use when mating the FPC and the connector.
ZIF connectors in FPCs use zero insertion force, hence the ZIF type. They lock down easily when inserted into the FPC using mechanisms such as:
- Front flip locking
- Slider cover locking
- Backflip locking
Non-ZIF connectors require some effort to be inserted. Unlike ZIF-type FPC connectors, they use friction instead of a lock mechanism. The surface friction between the FPC and contact pins keeps them in place.
Summary
If you are in the market for FPCs or FFC for your electrical unit project, trust WellPCB to produce the circuits and cables according to your specifications.
We deliver the circuits with the required connector types, pitches, and terminals. Grab the phone and let our team provide you with a quote for your project.
Alternatively, please send us an email or send a live chat query.





