Contents
What is an NFC Antenna?
NFC antennas help to transmit data to NFC devices. Interestingly, the NFC antennas feature loop structures and operate at low frequencies.
In truth, NFC is a communication method that requires short distances. As a result, the NFC Antenna’s design is simple and easy.
Additionally, NFC antennas utilize a fast two-way read and write operation over a range of detection distances from non-metallic and metallic substrates. Therefore, NFC antennas are the go-to for RFID, payment systems, and device-pairing applications.
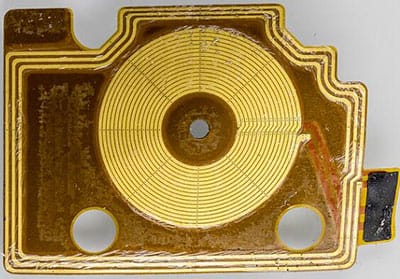
As for the structure, the Near Field Communication (NFC) antenna is a coil inductor paired with capacitors that form a parallel resonant LC tank.
How do NFC Antennas Work?
In the field communication world, you need two devices to establish NFC. They include one active NFC device (NFC-equipped smartphone or NFC reader) alongside a passive device (NFC tag).
So, when the active device generates a local magnetic field, it induces an electrical current in the passive device’s antenna.
Additionally, the electrical current in the antenna powers up the NFC chip. Then, it creates another magnetic field that the active device can read, allowing data transfer.
NFC antennas have excellent designs that allow them to resonate at the desired 13.56 MHz frequency. Their design also ensures that the operation is effective.
An NFC antenna with a poor design usually has the wrong tuning and doesn’t resonate at an ideal frequency. So, not all NFC tags would have the same scan distance performance.
Also, it’s important to note that the thickness of an NFC antenna does not affect its performance. For this reason, you’ll find that NFC antennas are thin.
Size and Shape of NFC Antennas
The size of your NFC antenna is another factor that affects performance. In truth, an NFC antenna’s reading distance increases according to its size. In other words, the bigger the antenna, the longer the reading range.
NFC antennas also have different shapes, each with a specific function. These shapes include:
- Rectangular NFC antennas: these NFC antennas boast a tremendous overall performance and an excellent operating volume. However, its proximity to metal can reduce its performance. Luckily, ferrite-backed options can solve this issue.
- Round NFC antennas: the round-shaped NFC antenna is similar to the rectangular-shaped variants, and you can also solve its metal proximity issues with some ferrite shielding.
- Wire-wound ferrite core tag antennas: the wire-wound NFC antennas work best for applications with spaces confined to one axis. Also, it works for a more extended range in a particular axis.
NFC Antenna Design: Things to Consider
There are two vital things to consider when designing your NFC antenna. They include the optimum read range and reliability of your NFC device. So, your first step should be to consider your requirements.
Designing the right antenna depends on the application’s requirements. You can start by finding out what you need before adding other requirements.
Then, consider the features and form factors of your final product. Also, the available space and boundaries for your NFC antenna are worth considering.
With this, you’ll get a clearer idea of the kind of antenna you want. For instance, if your application requires a maximum read range, you can’t use a low-power consumption design.
NFC Antenna Design Steps
1. Choose an NFC product.
2. Choose a Ctun value and fix the F0 target, then calculate the LA based on the Ctun and F0.
3. Next, define the dimensions of the antenna and matrix.
4. Design the matrix using the following: LA, LA divided by 5%. LA – 5%.
5. Create and characterize coil prototypes.
6. Then, choose the bast coil parameters.
7. Afterward, define the second run parameters and antenna matrix.
8. Design the matrix using the following: LA, LA divided by 2%. LA – 2%.
9. Differentiate the coil prototypes and choose the bast coil parameters.
The above picture shows the complete process required to design an NFC antenna.
Other Antenna Options
You can find etched antennas on NFC inlays or stickers. However, the more advanced high-quality disc tags and NFC products like keyfobs and wristbands use other antenna alternatives. The alternatives come in two categories: copper wire coil and PCB antennas.
Copper wire coil antennas usually have great scan distances. And the number of turns can effectively increase its length for a wider read range.
On the other hand, PCB antennas are double-sided PCBs. Hence, you can etch the antenna on both sides to increase the antenna’s length effectively.
If you make them correctly, PCB antennas can ensure excellent performance and high reliability. However, these antennas have more expensive industrial tags.
NFC Antenna Testing
You can carry out the following tests to check the performance of your NFC antenna:
- NFC Forum tests: this test is useful for NFC forum devices like mobile phones, P2P, and reader & card modules. Also, you can get an NFC compliance certificate after doing a compulsory NFC forum test for NFC forum devices.
- ISO/IEC 14443 tests: it’s ideal for PICC/PCD, type A and B with 106, 212, 424, and 848 kbps bit rates.
- EMVCo tests: it works for PICC/PCD, types A and B, with only 106 kbps bit rates.
FAQS
How Big Can an NFC Be?
The size of your NFC antenna depends on your application. Generally, larger antenna sizes offer more reading ranges. But be careful not to make it bigger than required.
Can you Amplify NFC?
Getting a wide range with an NFC device is impossible. So you can’t amplify NFC.
How Do I Connect My NFC Antenna?
Using an NFC tag, you can connect your antenna coil to pins 2 and 3 on the IC.
What is an NFC Antenna Used For?
NFC antennas work for NFC-compliant mobiles, wallets, data loggers, payment readers, payment services, NFC cards like bank cards, RFID security, and other applications.
Final Words
NFC antennas are crucial components of any NFC device. Without it, there will be no communication between NFC devices in a shorter range.
As we mentioned earlier, NFC antennas are different from regular antennas. They are coil inductors that operate at low frequencies and convert nearby magnetic fields into energy.
Do you have any questions about NFC tags and antennas? Feel free to contact us, and we’ll be happy to help.